Wed 14 Mar 2012
The most interesting thing(s) I’ve read in the last week
Posted by PJ under forensics, genetics, history, reading, this week, writing
No Comments
I read a number of interesting things in the last week and it’s been difficult choosing “most interesting,” so I’ve settled on something of a smorgasbord. First up, two somewhat-related articles:
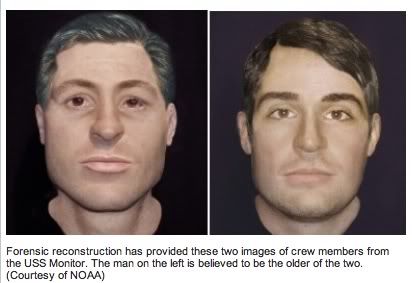
Nearly 150 years after they went down with their ship in a fierce Cape Hatteras storm, two members of the crew of the famed Civil War ironclad USS Monitor have come back to life in the form of newly created facial reconstructions.
Since it was discovered in 1991, preserved in 5,300 years’ worth of ice and snow in the Italian Alps, the body of the so-called Tyrolean Iceman has yielded a great deal of information. Scientists have learned his age (about 46), that he had knee problems, and how he died (by the shot of an arrow).
Now, researchers have sequenced the complete genome of the iceman, nicknamed Ötzi, and discovered even more intriguing details. They report in the journal Nature Communications that he had brown eyes and brown hair, was lactose intolerant and had Type O blood.

Honorable mentions:
A Romani Mystery from Dr. Beachcombing’s Brizarre History
Scientists found Romani mitochondrial DNA in a cemetery in Norwich in East Anglia in use from the tenth to eleventh centuries when conventional wisdom says they didn’t arrive in England until the 17th century.
And Scott Turow on how lack of competition amongst booksellers hurts authors.
